I. General Temperature Standards for Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics refers to the process of transporting goods from one temperature zone to another within a controlled temperature range, ensuring the quality and safety of the goods. Cold chains are widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industries, playing a crucial role in quality and safety assurance. The general temperature range for cold chains is between -18°C and 8°C, but different types of goods require different temperature ranges.
1.1 Common Cold Chain Temperature Ranges
The temperature range for cold chains varies depending on the type of goods. The common cold chain temperature ranges are as follows:
1. Ultra-Low Temperature: Below -60°C, such as liquid oxygen and liquid nitrogen.
2. Deep Freezing: -60°C to -30°C, such as ice cream and frozen meats.
3. Freezing: -30°C to -18°C, such as frozen seafood and fresh meat.
4. Deep Freeze: -18°C to -12°C, such as surimi and fish meat.
5. Refrigeration: -12°C to 8°C, such as dairy products and meat products.
6. Room Temperature: 8°C to 25°C, such as vegetables and fruits.
1.2 Temperature Ranges for Different Types of Goods
Different types of goods require different temperature ranges. Here are the temperature range requirements for common goods:
1. Fresh Food: Generally needs to be kept between 0°C and 4°C to maintain freshness and taste, while preventing overcooling or spoilage.
2. Frozen Food: Needs to be stored and transported below -18°C to ensure quality and safety.
3. Pharmaceuticals: Require strict storage and transport conditions, typically kept between 2°C and 8°C.
4. Cosmetics: Need to be kept within the appropriate temperature range during transport to prevent moisture or spoilage, usually stored between 2°C and 25°C, depending on the product type.
II. Special Temperature Standards for the Pharmaceutical and Food Industries
2.1 Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Transport
In pharmaceutical cold chain transport, besides the common -25°C to -15°C, 2°C to 8°C, 2°C to 25°C, and 15°C to 25°C temperature requirements, there are other specific temperature zones, such as:
– ≤-20°C
– -25°C to -20°C
– -20°C to -10°C
– 0°C to 4°C
– 0°C to 5°C
– 10°C to 20°C
– 20°C to 25°C
2.2 Food Cold Chain Transport
In food cold chain transport, besides the common ≤-10°C, ≤0°C, 0°C to 8°C, and 0°C to 25°C temperature requirements, there are other specific temperature zones, such as:
– ≤-18°C
– 10°C to 25°C
These temperature standards ensure that both pharmaceuticals and food products are transported and stored under conditions that maintain their quality and safety.
III. Importance of Temperature Control
3.1 Food Temperature Control
3.1.1 Food Quality and Safety
1. Temperature control is crucial for maintaining food quality and ensuring consumer health. Temperature fluctuations can lead to microbial growth, accelerated chemical reactions, and physical changes, affecting food safety and taste.
2. Implementing temperature control management during food retail logistics can effectively reduce the risk of food contamination. Proper storage and transportation conditions help inhibit the growth of bacteria and other harmful organisms, ensuring stable food quality. (Refrigerated food must be kept below 5°C, and cooked food must be kept above 60°C before consumption. When the temperature is kept below 5°C or above 60°C, the growth and reproduction of microorganisms slow down or stop, effectively preventing food spoilage. The temperature range of 5°C to 60°C is the danger zone for food storage. Cooked food stored at room temperature, especially in hot summer weather, should not be left out for more than 2 hours; even when stored in the refrigerator, it should not be kept for too long. Before consumption, reheating is necessary to ensure the food center temperature reaches above 70°C, with adequate heating time depending on the size, heat transfer properties, and initial temperature of the food to achieve thorough sterilization.)
3.1.2 Reducing Waste and Lowering Costs
1. Effective temperature control management can reduce losses and waste caused by food spoilage and damage. By monitoring and adjusting temperatures, the shelf life of food can be extended, reducing returns and losses, and improving supply chain efficiency.
2. Implementing temperature control management can lower operating costs. By optimizing energy consumption during storage and transportation and reducing potential issues such as refrigerant leaks, sustainable logistics goals can be achieved.
3.1.3 Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
1. Many countries and regions have strict temperature control regulations for food storage and transportation. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to legal disputes, economic losses, and damage to the company’s reputation.
2. Food retail companies need to follow international and domestic standards, such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), to ensure food safety and quality.
3.1.4 Customer Satisfaction and Brand Reputation
1. Consumers are increasingly demanding fresh and safe food. High-quality temperature control management can ensure the quality and taste of food during distribution, enhancing customer satisfaction.
2. Providing consistently high-quality products helps build and maintain a good brand image, enhances market competitiveness, and attracts more loyal customers.
3.1.5 Market Competitive Advantage
1. In the highly competitive food retail industry, an efficient temperature control management system is a key differentiator. Companies with excellent temperature control capabilities can provide more reliable services and meet customer needs.
2. Temperature control management is also a significant way for food retailers to showcase their technological innovation and sustainable development, establishing a competitive advantage in the market.
3.1.6 Environmental Friendliness and Sustainable Development
1. Through precise temperature control management, food retail companies can reduce unnecessary energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability trends.
2. Using environmentally friendly refrigerants and temperature control technologies can further reduce environmental impact, helping companies fulfill social responsibilities and enhance their image.
3.2 Pharmaceutical Temperature Control
Pharmaceuticals are special products, and their optimal temperature range directly affects people’s safety. During production, transportation, and storage, temperature significantly impacts the quality of pharmaceuticals. Inadequate storage and transportation, especially for refrigerated medicines, can lead to reduced efficacy, spoilage, or increased toxic side effects.
For example, storage temperature affects pharmaceutical quality in several ways. High temperatures can affect volatile components, while low temperatures can cause some pharmaceuticals to spoil, such as emulsions freezing and losing their emulsifying capacity after thawing. Temperature changes can alter the properties of pharmaceuticals, affecting oxidation, decomposition, hydrolysis, and the growth of parasites and microorganisms.
The storage temperature greatly influences the quality of pharmaceuticals. High or low temperatures can cause fundamental changes in pharmaceutical quality. For instance, injection solutions and water-soluble drugs can crack if stored below 0°C. Different pharmaceutical states change with temperature, and maintaining optimal temperature conditions is essential for quality assurance.
The impact of storage temperature on the shelf life of pharmaceuticals is significant. The shelf life refers to the period during which the pharmaceutical quality remains relatively stable under specific storage conditions. According to an approximate formula, raising the storage temperature by 10°C increases the chemical reaction speed by 3-5 times, and if the storage temperature is 10°C higher than the specified condition, the shelf life reduces by 1/4 to 1/2. This is particularly critical for less stable drugs, which may lose efficacy or become toxic, endangering users’ safety.
IV. Real-Time Temperature Control and Adjustment in Cold Chain Transport
In food and pharmaceutical cold chain transport, refrigerated trucks and insulated boxes are commonly used. For large orders, refrigerated trucks are generally chosen to reduce transport costs. For smaller orders, insulated box transport is preferable, offering flexibility for air, rail, and road transport.
– Refrigerated Trucks: These use active cooling, with refrigeration units installed to regulate the temperature inside the truck.
– Insulated Boxes: These use passive cooling, with refrigerants inside the boxes to absorb and release heat, maintaining temperature control.
By selecting the appropriate transport method and maintaining real-time temperature control, companies can ensure the safety and quality of their products during cold chain logistics.
V. Huizhou’s Expertise in This Field
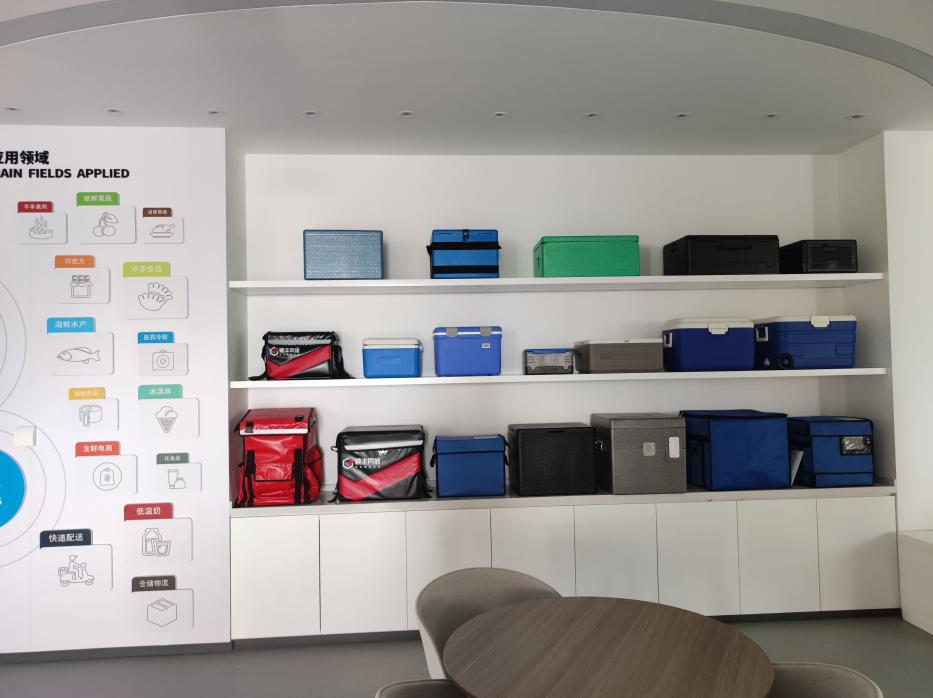
Huizhou specializes in the research, development, production, and testing of insulation boxes and refrigerants. We offer a variety of insulation box materials to choose from, including:
– EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) Insulation Boxes
– EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) Insulation Boxes
– PU (Polyurethane) Insulation Boxes
– VPU (Vacuum Panel Insulation) Boxes
– Aerogel Insulation Boxes
– VIP (Vacuum Insulated Panel) Insulation Boxes
– ESV (Enhanced Structural Vacuum) Insulation Boxes
We categorize our insulation boxes by usage frequency: single-use and reusable insulation boxes, to meet different customer needs.
We also provide a wide range of organic and inorganic refrigerants, including:
– Dry Ice
– Refrigerants with phase change points at -62°C, -55°C, -40°C, -33°C, -25°C, -23°C, -20°C, -18°C, -15°C, -12°C, 0°C, +2°C, +3°C, +5°C, +10°C, +15°C, +18°C, and +21°C
Our company is equipped with a chemical laboratory for the research and testing of various refrigerants, utilizing equipment such as DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry), viscometers, and freezers with different temperature zones.
Huizhou has established factories in major regions across the country to meet nationwide order demands. We are equipped with constant temperature and humidity equipment for testing the insulation performance of our boxes. Our testing laboratory has passed the CNAS (China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment) audit.
VI. Huizhou Case Studies
Pharmaceutical Insulation Box Project:
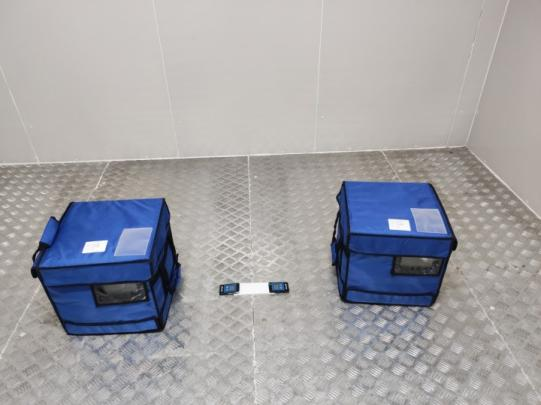
Our company produces reusable insulation boxes and refrigerants for pharmaceutical transportation. The insulation temperature zones of these boxes include:
– ≤-25°C
– ≤-20°C
– -25°C to -15°C
– 0°C to 5°C
– 2°C to 8°C
– 10°C to 20°C
Single-Use Insulation Box Project:
We manufacture single-use insulation boxes and refrigerants for pharmaceutical transportation. The insulation temperature zone is ≤0°C, primarily used for international pharmaceutical
shipments.
Ice Pack Project:
Our company produces refrigerants for fresh goods transportation, with phase change points at -20°C, -10°C, and 0°C.
These projects demonstrate Huizhou’s commitment to providing high-quality, reliable solutions for temperature-controlled logistics across various industries.